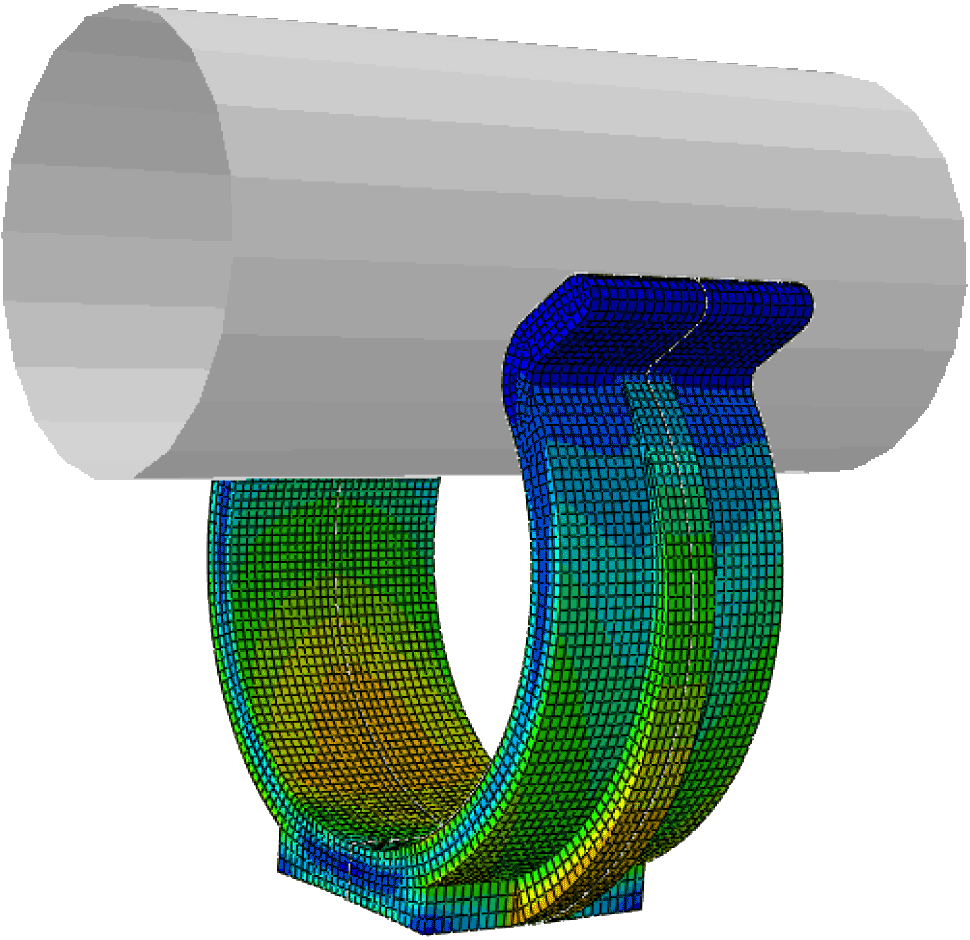
Industries including Automotive, Bio-medical and Consumer Goods
General testing capability with cyclic, cyclic-hold, creep and relaxation modes
General finite-strain viscoplasticity, hyper-viscoelasticity, back stress and creep mechanisms
Excellent results in hysteresis including Payne effect (strain amplitude dependent dynamic modulus)
Coupled with failure models in explicit simulations
Polymer materials found in engineering components and consumer goods, which are widely used in day-to-day life, are known for their complexity in modeling. Most solid polymers (polyolefins, TPU, TPE, etc.) exhibit nonlinear elasticity, nonlinear viscoelasticity, rate-dependent plasticity, pressure dependent yield, non-linear modulus changes and/or damage due to hard-soft phases changing morphology, and nonlinear hyper-kinematic hardening at large strains. Successful modeling of these materials therefore should incorporate all these effects. Unlike a user subroutine that is developed for a specific mathematical model, hence supporting only one or two mechanisms of interest, NWN Z-mat Framework supports all of these mechanisms, and several mathematical models.
Framework
Within a single generalized multiplicative finite strain framework for hyper-viscoelastic, viscoplastic and back stress behavior, NWN Z-mat supports many models for polymers (G’Sell, Arruda-Boyce viscoplasticity, Zener hyper-viscoelasticity, generalized two-layer, for example). In this framework it extremely easy to add, say, another kinematic hardening model, over and above what is already available, while continuing to support all other mechanisms and their models.
Hyperelasticity
About 10 different widely used models.
Viscoelasticity
Linear and nonlinear viscoelasticity including temperature shift functions.
Mullins
Two models of pseudo-elasticity or Mullins effect
Plasticity / viscoplasticity
Several yield criteria and flow rules with isotropic hardening/softening laws.
Kinematic hardening
Either integrated hypo-kinematic hardening (many models) which simulate hysteresis or hyper-viscoelastic back stresses like Arruda-Boyce 3 or 8 chain back stresses for lock-stretch effects.